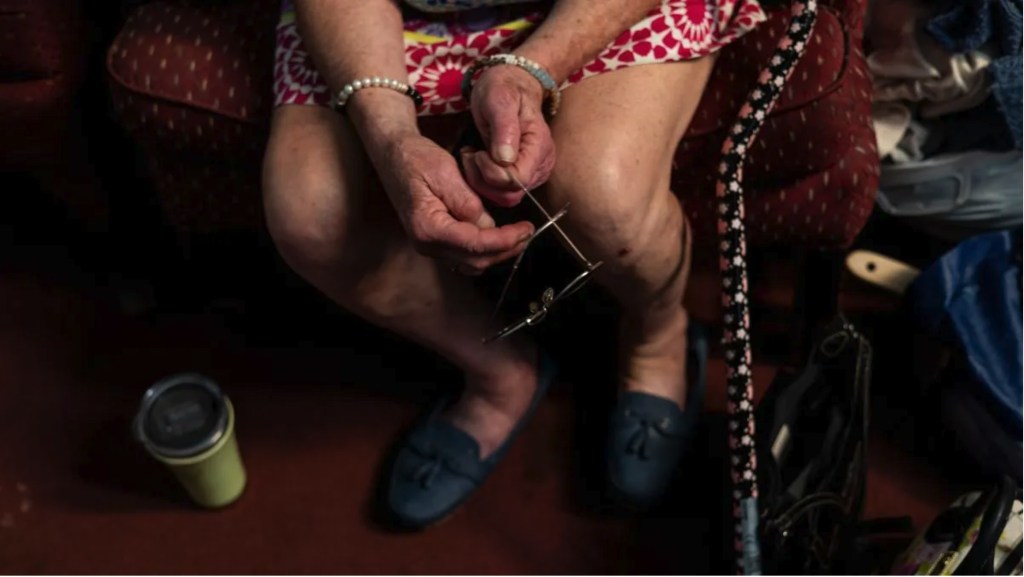
The number of Medicare patients in Maine receiving buprenorphine treatment for opioid addiction surged by approximately 70 percent between 2019 and 2023. This significant increase highlights a growing concern regarding the impact of the opioid crisis on the state’s older population, which has often been overlooked in discussions about addiction.
This analysis, conducted by the Maine Monitor, reveals that more seniors are grappling with substance use disorders, prompting a need for targeted interventions and support systems. The findings indicate a shift in the demographic affected by opioid addiction, traditionally perceived as a challenge primarily among younger individuals.
Rising Demand for Treatment
The rise in buprenorphine prescriptions is a response to the escalating opioid crisis that has plagued the United States for over two decades. Buprenorphine, a medication-assisted treatment, plays a crucial role in helping individuals manage addiction by reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings. As the opioid epidemic evolves, healthcare providers in Maine are adapting their strategies to address the unique needs of older adults.
The data collected reflects the changing landscape of opioid addiction, with many older adults facing the dual challenges of chronic pain management and the risk of opioid dependency. As these individuals age, their vulnerability to addiction increases, necessitating a reevaluation of how healthcare systems approach substance use treatment for seniors.
Healthcare Challenges and Solutions
Despite the increase in buprenorphine use, challenges remain in ensuring that older adults have access to necessary treatments. Many may encounter barriers, such as stigma associated with addiction, lack of awareness about available resources, or logistical issues in accessing healthcare facilities.
Advocates are calling for improved education and training for healthcare providers to better identify and address substance use disorders in older patients. There is a pressing need for comprehensive programs that not only provide medication-assisted treatment but also incorporate counseling and support networks tailored for seniors.
The Maine Monitor’s analysis underscores the importance of recognizing and addressing the opioid crisis among the state’s elderly population. As the number of individuals seeking treatment grows, the implications for public health policy and resource allocation will be significant.
In conclusion, the sharp rise in buprenorphine treatment among Medicare patients in Maine reflects a critical shift in the understanding of opioid addiction. As more seniors struggle with this issue, it is essential for healthcare systems to adapt and provide the necessary support to this vulnerable demographic.