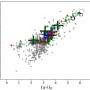
Recent observations conducted using the Anglo-Australian Telescope have revealed that the nearby galactic globular cluster known as NGC 6569 is actively losing stars through a process termed tidal stripping. The findings, published on December 22, 2023, on the arXiv preprint server, shed light on the dynamics at play within this fascinating astronomical structure.
Tidal stripping occurs when the gravitational forces from a larger galactic entity exert influence over a smaller cluster, causing stars to be pulled away. This phenomenon is particularly notable in NGC 6569, which is located approximately 30,000 light-years from Earth. The researchers utilized advanced observational techniques to analyze the interactions between the cluster and its surrounding environment.
Significance of the Findings
The implications of these observations extend beyond NGC 6569. Understanding star loss in globular clusters can provide critical insights into the evolutionary processes of galaxies. The study highlights how smaller clusters may be affected by gravitational interactions, potentially altering their composition and lifespan.
According to the research team, led by astronomers at the Australian National University, the data indicates that NGC 6569 is not only losing stars but may also be undergoing significant structural changes. This raises questions about the stability of such clusters in relation to their host galaxies.
The findings align with previous studies that suggest tidal interactions play a vital role in the evolution of star clusters. By examining NGC 6569, astronomers can better understand the broader context of star formation and loss in the universe.
The Future of Galactic Studies
As astronomers continue to explore the complexities of galactic structures, observations like those of NGC 6569 will be pivotal. The advanced capabilities of telescopes like the Anglo-Australian Telescope enable researchers to gather more detailed data, paving the way for future studies that could refine our understanding of galaxy dynamics.
The research adds to a growing body of work that emphasizes the importance of observational astronomy in unveiling the mysteries of the universe. With ongoing advancements in technology and methodology, scientists are poised to make further significant discoveries in the realm of star clusters and their behavior.
Overall, the findings regarding NGC 6569 represent a crucial step forward in galactic research, underscoring the dynamic nature of the cosmos and the ever-evolving narrative of star clusters.