The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has officially revised its recommendations regarding the Hepatitis B vaccine for infants. As of October 2023, the agency no longer advises that all newborns receive a dose of the vaccine within 24 hours of birth. This change follows recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) and has sparked considerable debate among healthcare professionals and parents.
Under the previous guidelines, all infants were recommended to receive the first dose of the Hepatitis B vaccine shortly after birth. The CDC’s decision to modify this protocol has raised concerns about potential risks and benefits. Proponents of the change argue that it allows for more individualized vaccination schedules based on the mother’s Hepatitis B status and the overall health of the newborn.
The CDC’s new policy suggests that the first dose of the Hepatitis B vaccine can be administered at any point during the first year of life, rather than strictly within the first 24 hours. This alteration aims to enhance flexibility in vaccination practices while still ensuring that infants receive necessary immunizations.
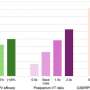
Critics of the decision worry that delaying the vaccine may increase the risk of Hepatitis B transmission, particularly in regions where the infection remains prevalent. The Hepatitis B virus can lead to serious health complications, including liver disease and cancer. According to the CDC, about 850,000 people in the United States are living with chronic Hepatitis B.
In response to the controversy, the CDC has emphasized that parents should consult with their healthcare providers to determine the best vaccination schedule for their children. The agency maintains that the benefits of the vaccine far outweigh the risks, and it continues to support vaccination as a critical public health measure.
The decision follows a trend observed in various health organizations to reassess vaccination schedules in light of new research and changing health landscapes. The CDC’s move also aligns with a growing emphasis on personalized medicine, which seeks to tailor medical treatments to individual patient needs.
As this policy unfolds, healthcare providers and parents alike will be closely monitoring the implications of the CDC’s revised guidelines. The conversation about infant vaccinations remains crucial, and clarity from health authorities will play a significant role in guiding public opinion and practice moving forward.