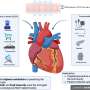
A recent study published in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings has revealed that financial strain and food insecurity significantly accelerate biological aging and increase the risk of mortality. This research highlights how social determinants of health (SDoH) can play a crucial role in cardiovascular health, often overshadowing traditional risk factors such as smoking and high blood pressure.
The analysis emphasizes that the impact of these social risk factors is profound and multifaceted. Researchers found that individuals facing economic hardships and lacking access to nutritious food are more likely to experience accelerated cardiac aging. The study suggests that these elements should be prioritized in discussions about heart health and preventive care strategies.
Understanding the Impact of Financial Strain
Financial strain is characterized by the stress and anxiety associated with managing limited resources. The study highlights that this stress can lead to physiological changes in the body, potentially resulting in cardiovascular diseases. Individuals struggling to meet basic needs often experience heightened levels of cortisol, a hormone linked to stress, which can adversely affect heart health over time.
Food insecurity, defined as the lack of consistent access to enough food for an active, healthy life, is also a significant factor. The analysis indicates that those who regularly face food shortages may have poorer dietary habits, which can lead to obesity and other health issues that further exacerbate heart problems.
The findings call for a shift towards more comprehensive health care approaches that incorporate social factors. Preventive interventions that address these issues could significantly improve patient outcomes.
Need for Targeted Preventive Interventions
Given the strong correlation between these social determinants and cardiovascular health, the study advocates for targeted preventive interventions. Health care providers are encouraged to consider social risk factors during patient assessments. This approach could help identify at-risk individuals and tailor interventions that address both their medical and social needs.
Patient-centered care is essential in this context. By understanding the broader circumstances that affect patients’ health, healthcare professionals can devise strategies that not only manage existing conditions but also prevent future health complications.
In summary, the findings from the Mayo Clinic Proceedings underscore the importance of recognizing financial strain and food insecurity as critical factors in cardiac health. Addressing these issues through targeted interventions and a holistic approach to patient care may help mitigate the risks associated with accelerated heart aging and improve overall health outcomes.