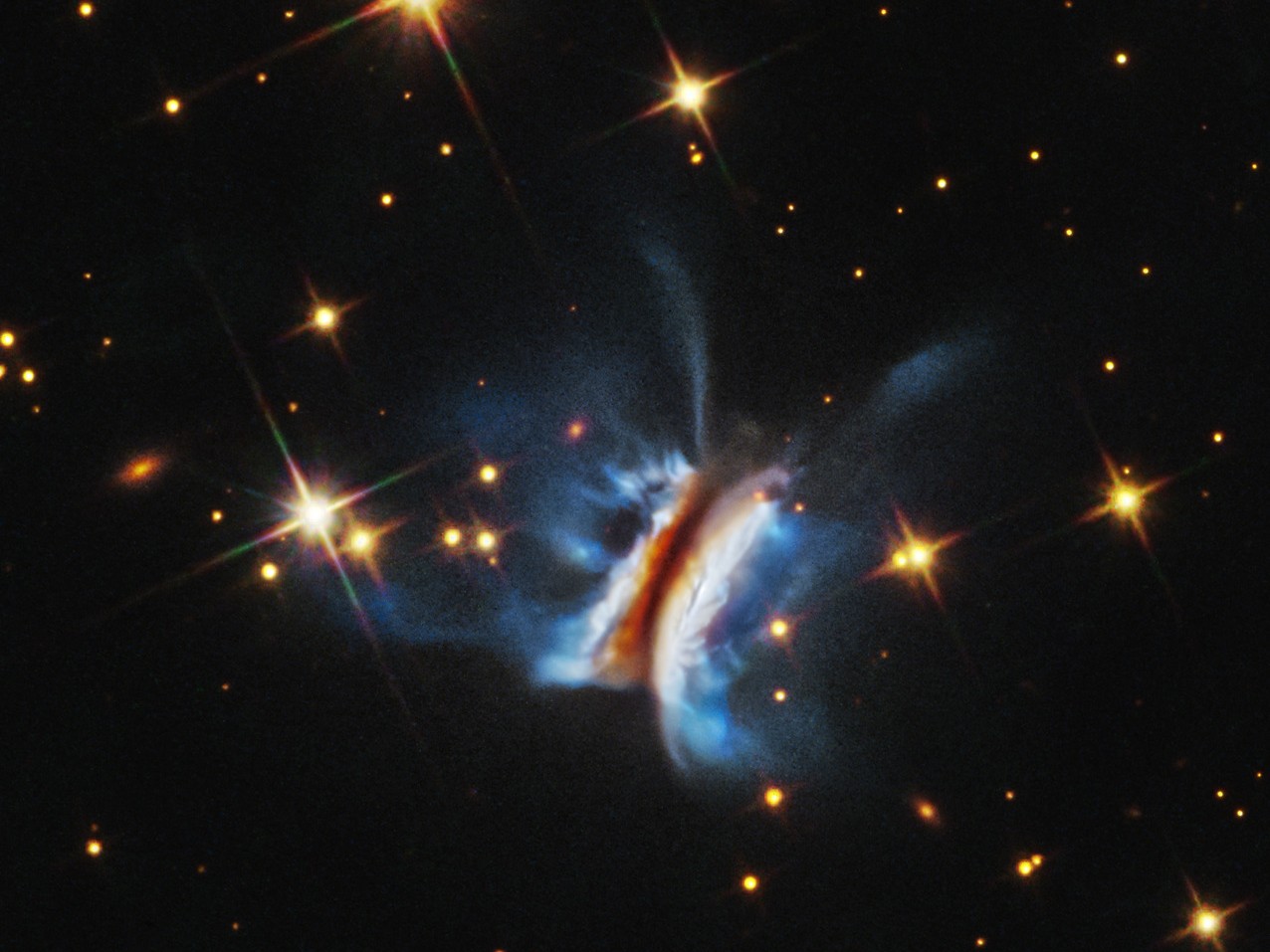
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled new findings regarding the turbulence present in one of the largest observed planet formation regions. This discovery, published in the *Astrophysical Journal*, enhances our understanding of how planets form within star-forming regions.
The observations focused on a colossal stellar nursery located approximately 1,000 light-years away in the constellation of Orion. This region, known as the Orion Nebula, serves as a significant site for studying the birth of stars and their accompanying planetary systems. Hubble’s advanced imaging capabilities allowed scientists to analyze the turbulent conditions that characterize this area, shedding light on the complex processes involved in planetary formation.
Insights from Hubble’s Observations
The findings reveal that the turbulence within the Orion Nebula plays a critical role in shaping the environment where planets develop. The intense activity in this region can influence the distribution of materials essential for planet formation, such as gas and dust. Kristina Monsch, a researcher at the Center for Astrophysics, noted that understanding these turbulent conditions is vital for comprehending how planets form and evolve in various environments across the universe.
Utilizing Hubble’s imaging technology, researchers gathered extensive data regarding the motions of gas and dust within the nebula. The turbulence has been observed to cause fluctuations in density, which can either promote or hinder the formation of new planets. This duality presents a complex challenge for astronomers as they work to decode the intricate mechanics of planetary birth.
Implications for Future Research
The implications of these findings extend beyond the Orion Nebula. Understanding the turbulence in stellar nurseries offers a broader perspective on planetary formation processes throughout the universe. As astronomers continue to explore various star-forming regions, the insights garnered from Hubble’s observations will help refine existing models of how planets come into being.
Joseph DePasquale, who contributed to the image processing of the data, emphasized the importance of such research in our quest to understand not just our solar system, but also the myriad of planetary systems beyond it. “The more we learn about these turbulent environments, the closer we get to answering fundamental questions about the universe,” he stated.
The findings from Hubble’s observations underscore the telescope’s vital role in expanding our knowledge of cosmic phenomena. As one of the most powerful tools in astronomy, Hubble continues to provide invaluable data that shapes our understanding of the universe and our place within it. The ongoing research in planetary formation will likely lead to further discoveries, enhancing our comprehension of the processes that govern star and planet development in the cosmos.