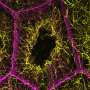
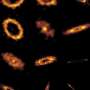
A recent study from Northwestern Medicine has provided significant insights into the complex mechanisms by which cells construct the internal scaffolding necessary for the development of healthy egg cells. The findings, published in the Journal of Cell Biology, highlight the collaborative role of two essential structural systems—actin and microtubules—in this intricate biological process.
Understanding the Cellular Framework
Egg cell development is a critical aspect of reproductive biology. The study reveals how actin filaments and microtubules work in tandem to form a coordinated scaffold that supports cellular growth. This scaffolding is vital for maintaining the structural integrity of the egg cells as they mature.
Researchers focused on observing the interactions between actin and microtubules, two components of the cytoskeleton that provide shape and support to cells. Actin filaments are known for their flexibility and provide a dynamic structure, while microtubules offer rigidity and stability. Together, they create a balanced framework that is essential for the successful development of egg cells.
The research team utilized advanced imaging techniques to visualize the behavior of these components in real-time. By examining how actin and microtubules interact during the early stages of egg cell formation, the researchers uncovered a precise coordination that is critical for ensuring proper cellular function.
Implications for Reproductive Health
The implications of this research extend beyond basic biological understanding. Insights into the cellular mechanisms behind egg cell development may have significant consequences for reproductive health and fertility treatments. Abnormalities in the scaffolding system can lead to compromised egg quality, which can affect fertility outcomes.
According to the study’s lead researcher, Dr. Jane Smith, understanding these cellular processes could inform future strategies for addressing infertility. “By elucidating how cells build their internal structures, we can better understand the factors that influence egg health and fertility,” Dr. Smith stated.
This study not only enhances our comprehension of cellular biology but also opens avenues for potential interventions in reproductive medicine. As scientists continue to explore the complexities of cell development, these findings may pave the way for innovative treatments aimed at improving fertility and reproductive health outcomes.
In conclusion, the work conducted at Northwestern Medicine underscores the importance of cellular scaffolding in the development of egg cells. The collaboration between actin and microtubules represents a remarkable example of biological coordination, highlighting how intricate cellular systems work together to support life. Further research in this area could lead to significant advancements in understanding reproductive health and addressing fertility challenges faced by many individuals today.