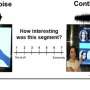
A recent study from Bar-Ilan University highlights that the engagement level of learners plays a more significant role in their attention than the presence of background noise. Researchers examined the effects of both external distractions and internal perceptions of interest while participants viewed a 35-minute educational video lecture.
The study involved 32 participants who were monitored for brain activity using Electroencephalography (EEG) and physiological responses through skin conductance. During the experiment, participants watched lecture segments presented in either a quiet environment or accompanied by background construction sounds, which included both continuous drilling and intermittent air-hammers.
Participants were asked to rate the interest level of the content throughout the video and answer comprehension questions to evaluate their understanding. This dual approach allowed researchers to measure not only how external factors like noise impacted attention but also how internal factors, such as personal interest in the material, influenced learning outcomes.
The findings suggest that when it comes to learning, fostering an engaging environment may be more beneficial than striving for complete silence. The study indicates that when participants found the lecture interesting, they were more likely to focus and retain the information, regardless of the noise level. This could have significant implications for educational settings, particularly in areas where background noise is unavoidable.
In addition to measuring engagement, the research sheds light on the complex relationship between attention and distraction. While it is common to assume that a quiet learning environment is ideal, this study challenges that notion by emphasizing the role of content engagement.
The results contribute to a growing body of literature exploring how various factors affect learning processes. By prioritizing engagement over eliminating distractions, educators might better tailor their teaching strategies to enhance student comprehension and retention.
As schools and universities continue to adapt to various learning environments, this research provides a vital insight into optimizing educational experiences. By focusing on making content more engaging, learning institutions may better support students in achieving their academic goals, even in less-than-ideal conditions.