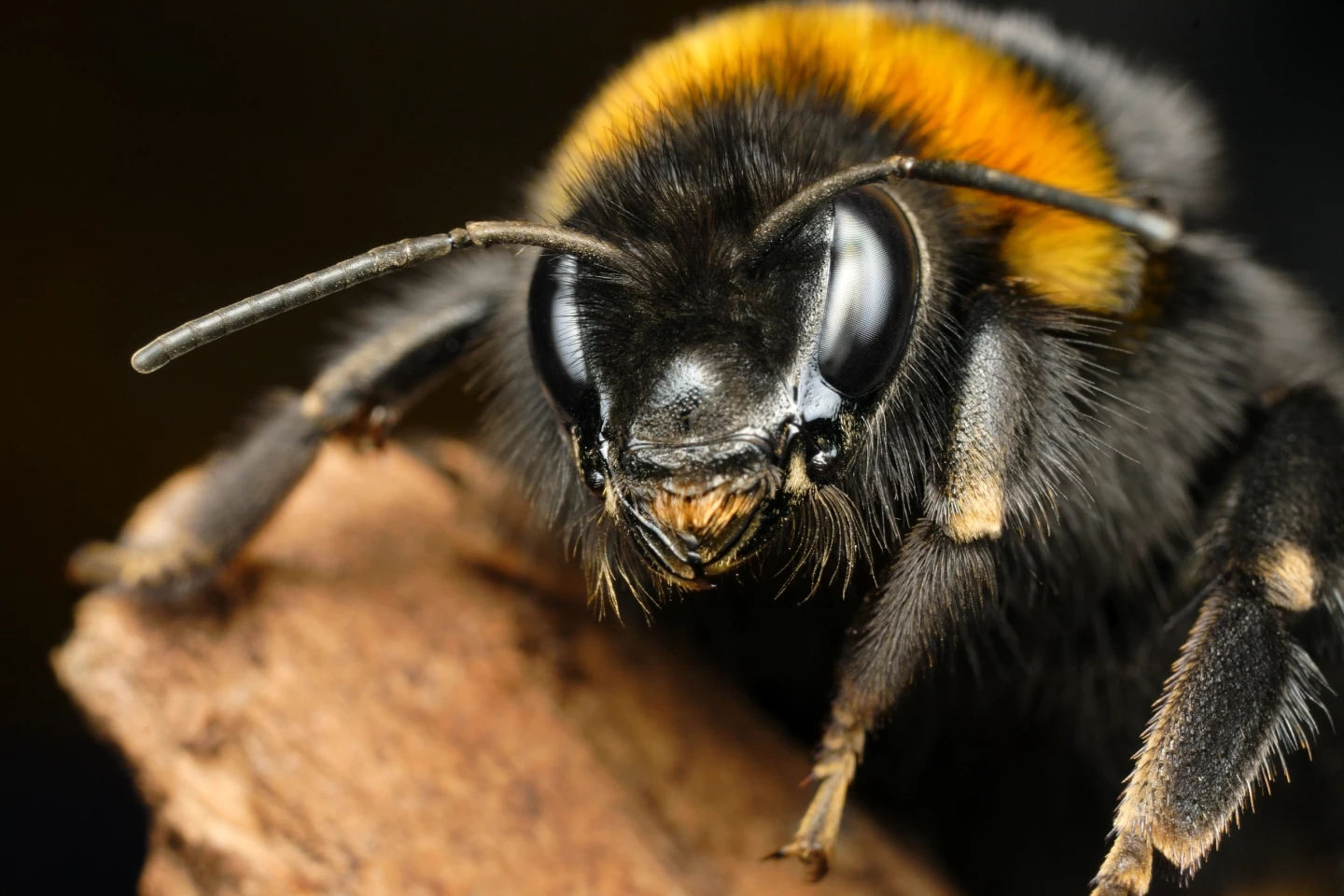
Recent research from Southern Medical University in China has revealed surprising insights into the social behavior of bumblebees, suggesting that these insects exhibit a form of “contagious positivity.” This study challenges the perception of bumblebees as simple creatures, highlighting complex interactions that occur within their colonies.
Researchers conducted experiments to observe how bumblebees communicate and share information. They discovered that when one bee demonstrates positive behavior, such as successfully locating food, this behavior is quickly adopted by others in the colony. This phenomenon is akin to a social contagion, where positive actions spread rapidly among individuals, enhancing collective foraging efficiency.
The findings indicate that bumblebees possess sophisticated social networks. Unlike many other insects, which may rely on pheromones or visual cues to communicate, bumblebees utilize a combination of both methods. This dual approach allows them to convey information about food sources and navigate their environment more effectively.
Understanding Bumblebee Behavior
The study involved observing bumblebee colonies in controlled environments, where researchers manipulated variables to see how bees reacted to positive stimuli. For instance, when one bee was rewarded for finding nectar, it was noted that surrounding bees would quickly follow suit, demonstrating heightened activity and engagement.
According to lead researcher Dr. Ying Zhang, “This study illustrates that bumblebees are capable of complex social interactions that play a crucial role in their survival. The positivity we observed is more than just cute behavior; it has significant implications for their foraging success.”
Bumblebees, often seen as charming and somewhat clumsy in their movement, are critical pollinators in many ecosystems. Their ability to communicate effectively and spread positive behavior may be vital for maintaining the health of their populations, especially in the face of environmental challenges.
Implications for Conservation
Understanding the social dynamics of bumblebees has broader implications for conservation efforts. As populations of these essential pollinators face decline due to habitat loss and pesticides, insights into their behavior can inform strategies for protection and restoration.
The research emphasizes the importance of preserving habitats that support bumblebee colonies. By fostering environments where these insects can thrive, conservationists may enhance not only the health of bee populations but also the ecosystems that depend on them.
In summary, the study conducted by Southern Medical University reveals that bumblebees exhibit a form of social positivity that enhances their foraging behavior. This groundbreaking research sheds light on the complexities of bumblebee communication and its implications for their survival and the ecosystems they serve. The findings underscore the need for continued efforts to protect these vital pollinators in an ever-changing environment.