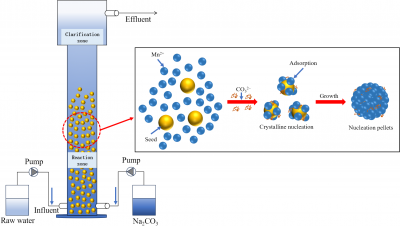
A recent study has unveiled a highly efficient method for recovering manganese ions from hydrometallurgical tailings water. The approach, known as the nucleation crystallization pelleting process, demonstrates significant potential in reducing both resource wastage and environmental impacts associated with mining operations.
The research highlights that this innovative process not only maximizes the recovery of manganese ions but also presents a practical solution to an ongoing environmental challenge. By effectively extracting high concentrations of manganese from waste water, the process addresses the dual concerns of resource efficiency and ecological sustainability.
Efficiency and Practicality of the New Method
The study showcases the operational efficiency of the nucleation crystallization pelleting technique. Researchers found that it can achieve high recovery rates, which is crucial given the increasing demand for manganese in various industrial applications. Manganese is essential for steel production and battery manufacturing, making its recovery from waste streams particularly valuable.
Importantly, the process has been tested in various conditions, confirming its versatility and adaptability. This research points to a significant advancement in hydrometallurgical practices, providing a method that can be integrated into existing systems with relative ease.
Environmental Implications and Future Prospects
The implications of this study extend beyond resource recovery. The nucleation crystallization pelleting process could play a vital role in minimizing the environmental footprint of mining operations. By reducing the volume of tailings water that typically leads to contamination and ecological harm, this method stands to foster more sustainable mining practices.
As the global push for sustainable development intensifies, solutions like this one are increasingly relevant. The findings of the study may contribute to broader efforts aimed at improving resource management and reducing environmental degradation. Further research and pilot projects will be essential to fully realize the potential of this technique and to implement it on a larger scale.
In conclusion, the nucleation crystallization pelleting process offers a promising avenue for the effective recovery of manganese ions from hydrometallurgical tailings water. As industries strive for greater sustainability, innovations like this could significantly reshape the landscape of resource recovery and environmental management.