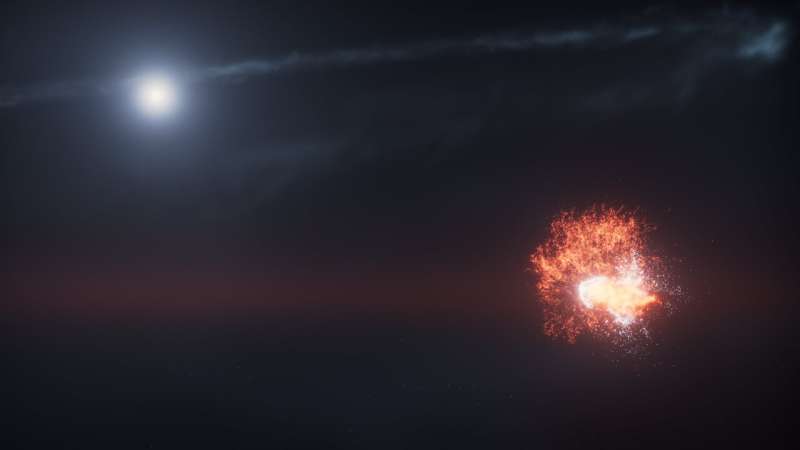
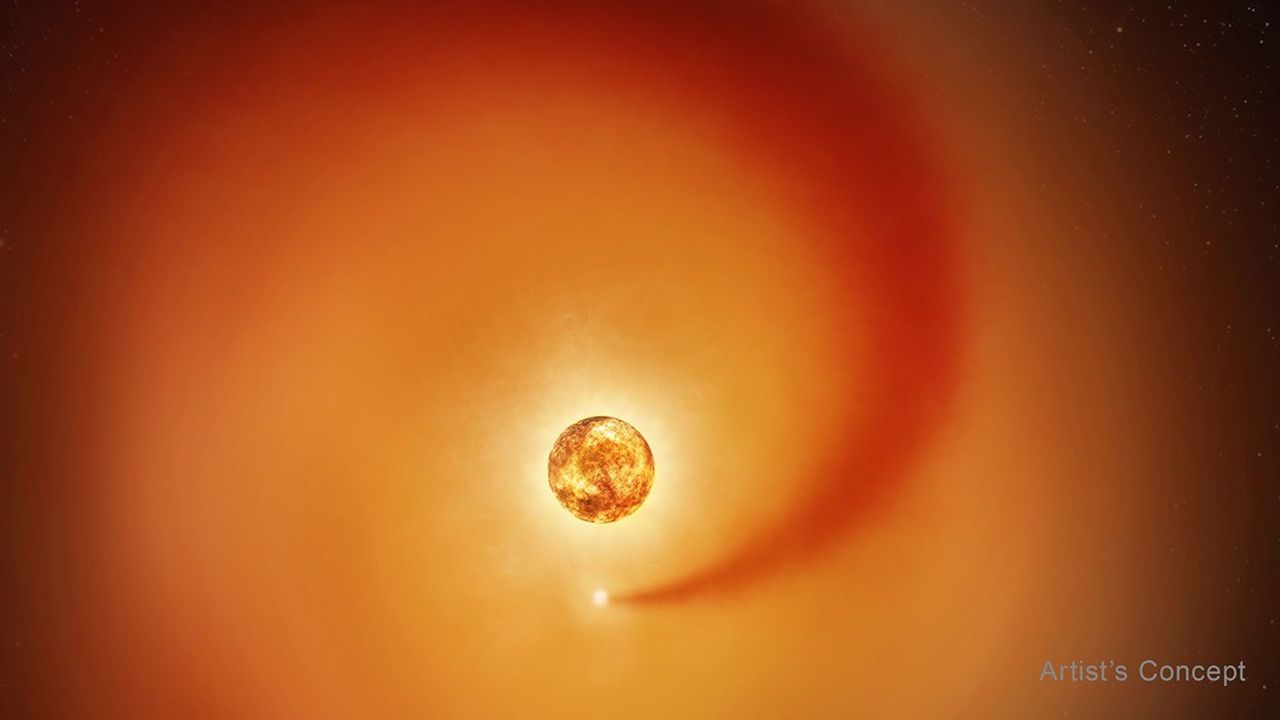
Astronomers have made a significant discovery regarding the red supergiant star Betelgeuse, confirming the presence of a hidden companion star named Siwarha. This revelation, made possible by observations from the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories, sheds light on the mysterious behavior of Betelgeuse, known for its unusual dimming and brightening patterns.
Scientists first identified Siwarha in July 2025, hypothesizing its influence on Betelgeuse’s erratic light output. Subsequent observations have now revealed a “wake” generated by this companion star, providing direct evidence of its existence. Andrea Dupree, the lead author of the study and an astronomer at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, emphasized the importance of this finding, stating, “With this new direct evidence, Betelgeuse gives us a front-row seat to watch how a giant star changes over time.”
The team utilized data from the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory in Arizona and the Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory in the Canary Islands alongside Hubble’s observations. They detected a pattern of changes in Betelgeuse’s light spectrum, which varied as Siwarha moved in its orbit. The wake, comprised of denser material than the surrounding gases of Betelgeuse’s atmosphere, alters the colors emitted by the star.
“It’s a bit like a boat moving through water,” Dupree explained. “The companion star creates a ripple effect in Betelgeuse’s atmosphere that we can actually see in the data.” This ripple effect will be observable again in 2027 when Siwarha crosses between Betelgeuse and Earth, prompting researchers to prepare for further observations.
The findings were presented at the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix, Arizona, and will be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The confirmation of Siwarha not only enhances our understanding of Betelgeuse’s characteristics but also contributes to the broader study of stellar evolution and the lifecycle of supergiant stars.
As astronomers continue to study Betelgeuse, the insights gained from Siwarha’s wake will likely provide crucial information about how massive stars evolve, shed material, and eventually explode as supernovae. The ongoing investigation into this dynamic duo exemplifies the exciting developments in modern astrophysics and the capabilities of advanced observational technology.